Understanding web analytics and search engine optimization (SEO) tools is important to the success of any website in today’s digital landscape. Web analytics tools provide businesses with insights into user behavior and website performance, while SEO tools ensure visibility in search engines Google Search Console vs Google Analytics are among the top tools in this area When used together, these tools provide powerful integration for search performance and better user engagement.
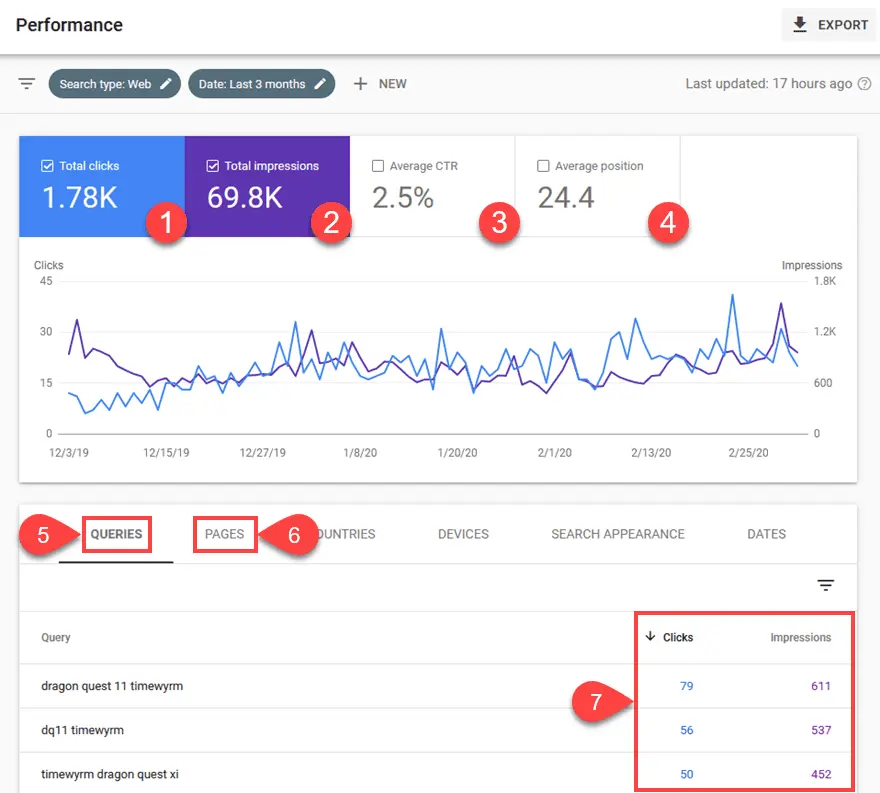
Overview of Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) is like a center where websites and website owners can see how their site performs on Google, including this free tool. As a tool, it is created to help webmasters understand better their website performance in search engines and easily access important data such as the coverage of your index or how users interact with SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages) for specific queries related directly to your business.
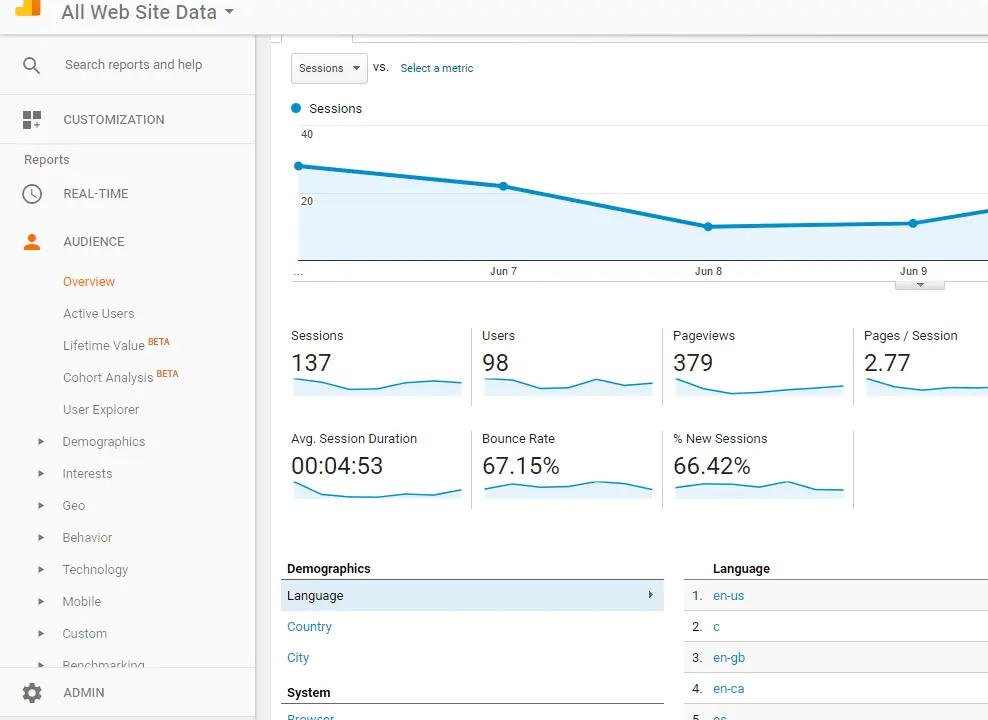
Overview of Google Analytics
Definition and Purpose
Google Analytics (GA) is a comprehensive web analytics tool that provides comprehensive insights into user behavior, traffic, and overall website usage Unlike GSC, which focuses on search data, GA is about tracking user interactions when they have visited your website.
Key Features of Google Search Console
• Search Analytics: GSC provides in-depth analysis of the search queries users enter to find your website, including metrics such as click-through rate (CTR), impressions, and rank.
• Crawl coverage: This feature ensures that your websites can be properly crawled and indexed by Google. If there are problems, such as blocked features or errors, GSC insists on immediate resolution.
• Mobile Usability: With mobile-first indexing becoming increasingly important, this feature helps ensure that your site is mobile-friendly and focuses on information about how to use mobile devices
• Security Information: GSC provides alerts about potential security breaches, malware, or any harmful activity that may affect your website.
• Core Web Vitals: These metrics track page-load speed, interactivity, and layout consistency—important ingredients for providing a smooth user experience.
Key Features of Google Analytics
• User Behavior Monitoring: GA tracks how users move through your website, including what pages they visit, how long they stay, and where they leave.
• Traffic metrics (page views, sessions): Tracks key metrics such as session count, unique visitors, and page views, giving you a clear picture of overall website traffic.
• Demographic and geographic insights: GA provides data about your audience demographics, including age, gender, and location, to help tailor content to specific groups.
• E-commerce tracking and targeting: For e-commerce websites, GA provides the ability to track purchases, transactions, and user journeys through the sales funnel A targeting system helps measure conversions, such as mailing forms or products which are sold.
Common Features Between Google Search Console and Google Analytics
Website Traffic Data
Both Google Search Console and Google Analytics provide website traffic data from different perspectives. GSC focuses on search-related traffic—how users find your site through Google searches—while GA provides a broader view of user behavior once visitors arrive on the site.
URL Performance
Both tools allow you to analyze the performance of individual URLs. In GSC, you can monitor how specific pages are performing in search results, while in GA, you can track user engagement with those pages.
Search Queries
Google Search Console gives keyword-level insights, allowing you to see what queries users type to reach your site. GA offers a broader view of search behavior but lacks detailed keyword insights. Together, they provide a more holistic view of search traffic.
Device and Geographic Data
Both tools offer insights into how users access your website, including the devices (desktop, mobile, tablet) they use and their geographic locations, helping to tailor your content and design to match audience needs.
Traffic Sources
GSC focuses primarily on organic search traffic, while GA breaks down traffic sources from organic, direct, referral, and paid channels. This broader perspective in GA allows for a comprehensive understanding of where your visitors are coming from.
Goal Chasing
In Google Analytics, you can set up goals to track conversions like sales, form submissions, or downloads. Google Analytics Search Console does not provide this functionality but can help identify the search queries and pages driving traffic toward your goal pages.
Combination
Both tools can be integrated for enhanced data analysis. Linking Google Search Console with Google Analytics allows you to combine search data with user behavior insights for more robust reporting and analysis.
Key Differences Between Google Search Console and Google Analytics
| Feature | Google Search Console | Google Analytics |
| Resolution | Focuses on search performance | Focuses on user behavior |
| Data Source | Data directly from Google's search engine | Data from user browsers and tracking code |
| Traffic Sources | Primarily organic search | Various sources, including paid ads |
| User Behavior Metrics | Limited metrics available | Comprehensive user behavior metrics |
| Goal Tracking | Not available | Available for tracking specific user actions |
| Audience Insights | Limited demographic information | Detailed audience insights |
| Integration with Other Platforms | Can link with GA | Integrates with various Google products |
How to Use Google Search Console and Google Analytics Together
1. Link Accounts for Integrated Visions: Start by linking Google Search Console with Google Analytics to combine search data with user behavior insights.
2. Analyze Organic Search Questions: Use GSC to understand which keywords drive traffic, then use GA to see how users engage with the site after arriving.
3. Track Click-Through Rates (CTR): Monitor CTR for high-impact keywords and optimize for better performance.
4. Identify High-Impact Pages: Use both tools to identify pages that perform well in search but may need optimization to increase engagement or conversions.
5. Set Up Goals and Conversion Chasing: In GA, set up specific goals (such as purchases or form submissions) and track how search traffic contributes to those conversions.
6. Analyze Bounce Rates for Improvement: High bounce rates may indicate issues with content or user experience. Use both tools to identify where visitors drop off.
7. Power Demographic Data for Targeted Content: GA’s demographic insights can guide you to create content that resonates with your audience.
8. Regularly Review Gaining Channels: In GA, track where your traffic comes from—organic search, social media, referrals—and adjust marketing strategies accordingly.
9. Optimize for Mobile Usability: Use GSC’s mobile usability report to identify and fix any issues on mobile devices.
10. Continuously monitor performance metrics: Both tools offer various performance metrics. Regular monitoring ensures your site stays optimized for search and user experience.
11. Stay Informed on SEO Best Practices: GSC alerts you to changes in search algorithms or penalties, helping you stay up-to-date on SEO best practices.
Conclusion
Using Google Search Console vs. Google Analytics in conjunction provides a proper picture of your website's overall performance.
GSC focuses on improving search performance, whereas GA lets you in on the user behavior, the conversion of a user as well as the traffic patterns. Present as the interrelation of both advantages with which you can develop a site that is both more visible and successful—both high engager and strategist. Formulate your marketing strategies based on the insights these two tools provide and continually be the leader of your market.

Comments
No comments yet.
Leave a Comment